|
COP
3 BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY 1996
PLEASE USE OUR A-Z INDEX
TO NAVIGATE THIS SITE
COP3
the third ordinary meeting of the parties to the convention took place in November 1996, in Buenos Aires,
Argentina.
Although a meeting is recorded as having taken place, it
appears that nothing was agreed to be recorded on the official
website, but several issues were discussed as follows:
Passing the
baton, Indonesia's Minister of Environment and COP-2 President Sarwono Kusumaatmadja handed over the leadership of the COP2 to COP-3 President Maria Julia Alsogaray, Secretary for Environment and Natural Resources.
UNEP Deputy Executive Director Reuben Olembo and GEF CEO Mohamed El-Ashry were among the speakers encouraging greater cooperation toward implementation of the CBD.
The sunny Argentine afternoon provided a pleasant setting for shirtsleeve informal negotiations by some delegates; in the Committee of the Whole, formal Working Group chairs John Ashe of Antigua and Barbuda and Terry Jones of the Seychelles summarized progress in their groups.
Malawi was not satisfied that the Intergovernmental Panel on Forests would sufficiently address biodiversity. Chile emphasized marine biodiversity, clearing-house mechanism, benefits sharing and agro-biodiversity as work programme elements. Wetlands International offered technical assistance toward cooperation with the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance.
Uganda called for a work programme on incentives. Senegal asked for information on the private sector's role in capacity building, and the
UK urged capacity building related to biosafety.
Representatives of indigenous peoples in Asia, Africa and the Pacific were among those calling on COP-3 delegates to establish an open-ended working group on indigenous and local communities, to fulfill a pledge from COP-2 to fill a position on the Secretariat Staff on this issue, and to increase indigenous and local communities participation in CBD deliberations and implementation.
Argentina called for support for countries that do not have Internet access. South Africa connected CHM user needs with access to financial resources.
Delegations debated agricultural biodiversity and the Convention's financial mechanism.
While the Committee of the whole debated technology transfer, intellectual property rights.
SUBSIDIARY
BODY ON SCIENTIFIC TECHNICAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL ADVICE
The
second meeting of the SBSTTA took place in Montreal, Canada,
between 2 - 6 September 1996, one month ahead of the
Conference of the Parties.

PARTIES
TO THE CONVENTION
As of 2016, the
Convention
on Biological Diversification had 196 parties, which includes 195 states and the European
Union. All UN member states - with the exception of the United
States - have ratified the treaty.
The
United Nations is the link between other Conferences of the
Parties to include Climate
Change and Desertification.
It is a bit confusing to have so many different conferences
that deal with interconnected issues. In addition, each member
state will have their own meetings on the subject to decide
what their position will be at the COPs. We wonder then at the
size of the carbon
footprints so generated in relation to the effectiveness
of the decisions - that at the moment do not appear to be
working to stabilize our climate, stop deserts from being
created, or protect the habitats of our species.
CONFERENCES
OF THE PARTIES
The convention's governing body is the Conference of the Parties (COP), consisting of all governments (and regional economic integration organizations) that have ratified the treaty. This ultimate authority reviews progress under the Convention, identifies new priorities, and sets work plans for members.
The Conference of the Parties (COP) uses expertise and support from several other bodies that are established by the Convention.
The main organs are:
(a)
review of progress in implementation;
(b) strategic actions to enhance implementation;
(c) strengthening means of implementation; and
(d)
operations of the convention and the Protocols.
National Reports
Parties prepare national reports on the status of implementation of the Convention.
MARINE & COASTAL BIODIVERSITY
The oceans occupy more than 70% of the Earth’s surface and 95% of the biosphere. Life in the sea is roughly 1000 times older than the genus Homo.
There is broad recognition that the seas face unprecedented human-induced threats from industries such as
fishing and transportation, the effects of waste disposal, excess nutrients from
agricultural runoff, and the introduction of exotic species.
If we fail to understand both the vulnerability and resilience of the living sea, the relatively brief history of the
human species will face a tragic destiny.
What's the Problem?
According to the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, the world’s oceans and coasts are highly threatened and subject to rapid environmental change. Major threats to marine and coastal ecosystems include:
* Land-based pollution and euthrophication
* Overfishing, destructive
fishing, and illegal, unreported and unregulated (IUU) fishing
* Alterations of physical habitats
* Invasions of exotic species
* Global climate change
CONTACTS
Cristiana Pașca Palmer
Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity
413, Saint Jacques Street, suite 800
Montreal QC H2Y 1N9
Canada
Tel: +1 514 288 2220
Fax: +1 514 288 6588
E-Mail: secretariat@cbd.int
Web: www.cbd.int
BIODIVERSITY
COP HISTORY
|
COP
1: 1994 Nassau, Bahamas,
Nov & Dec
|
COP
8: 2006 Curitiba, Brazil, 8
Mar
|
|
COP
2: 1995 Jakarta, Indonesia,
Nov
|
COP
9: 2008 Bonn, Germany,
May
|
|
COP
3: 1996 Buenos Aires, Argentina,
Nov
|
COP
10: 2010 Nagoya, Japan,
Oct
|
|
COP
4: 1998 Bratislava, Slovakia, May
|
COP
11: 2012 Hyderabad, India
|
|
EXCOP:
1999 Cartagena, Colombia, Feb
|
COP
12: 2014 Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, Oct
|
|
COP
5: 2000 Nairobi, Kenya, May
|
COP
13: 2016 Cancun, Mexico,
2 to 17 Dec
|
|
COP
6: 2002 The Hague, Netherlands,
April
|
COP
14: 2018
Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt, 17 to 29 Nov
|
|
COP
7: 2004 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, Feb
|
COP
15: 2020 Kunming, Yunnan, China
|
CLIMATE
CHANGE UN COP HISTORY
|
1995
COP 1, BERLIN, GERMANY
1996
COP 2, GENEVA, SWITZERLAND
1997
COP 3, KYOTO, JAPAN
1998
COP 4, BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA
1999
COP 5, BONN, GERMANY
2000:COP
6, THE HAGUE, NETHERLANDS
2001
COP 7, MARRAKECH, MOROCCO
2002
COP 8, NEW DELHI, INDIA
2003
COP 9, MILAN, ITALY
2004
COP 10, BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA
2005
COP 11/CMP 1, MONTREAL, CANADA
2006
COP 12/CMP 2, NAIROBI, KENYA
2007
COP 13/CMP 3, BALI, INDONESIA
|
2008
COP 14/CMP 4, POZNAN, POLAND
2009
COP 15/CMP 5, COPENHAGEN, DENMARK
2010
COP 16/CMP 6, CANCUN, MEXICO
2011
COP 17/CMP 7, DURBAN, SOUTH AFRICA
2012
COP 18/CMP 8, DOHA, QATAR
2013
COP 19/CMP 9, WARSAW, POLAND
2014
COP 20/CMP 10, LIMA, PERU
2015
COP 21/CMP 11, Paris, France
2016
COP 22/CMP 12/CMA 1, Marrakech, Morocco
2017
COP 23/CMP 13/CMA 2, Bonn, Germany
2018
COP 24/CMP 14/CMA 3, Katowice, Poland
2019
COP 25/CMP 15/CMA 4, Santiago, Chile
2020
COP 26/CMP 16/CMA 5, to be announced
|
DESERTIFICATION
COP HISTORY
|
COP
1:
Rome, Italy, 29 Sept to 10 Oct 1997
|
COP
9:
Buenos Aires, Argentina, 21 Sept to 2 Oct 2009
|
|
COP
2:
Dakar, Senegal, 30 Nov to 11 Dec 1998
|
COP
10:
Changwon, South Korea, 10 to 20 Oct 2011
|
|
COP
3:
Recife, Brazil, 15 to 26 Nov 1999
|
COP
11:
Windhoek, Namibia, 16 to 27 Sept 2013
|
|
COP
4:
Bonn, Germany, 11 to 22 Dec 2000
|
COP
12:
Ankara, Turkey, 12 to 23 Oct 2015
|
|
COP
5:
Geneva, Switzerland, 1 to 12 Oct 2001
|
COP
13:
Ordos City, China, 6 to 16 Sept 2017
|
|
COP
6:
Havana, Cuba, 25 August to 5 Sept 2003
|
COP
14:
New Delhi, India, 2 to 13 Sept 2019
|
|
COP
7:
Nairobi, Kenya, 17 to 28 Oct 2005
|
COP
15:
2020
|
|
COP
8:
Madrid, Spain, 3 to 14 Sept 2007
|
COP
16: 2021
|
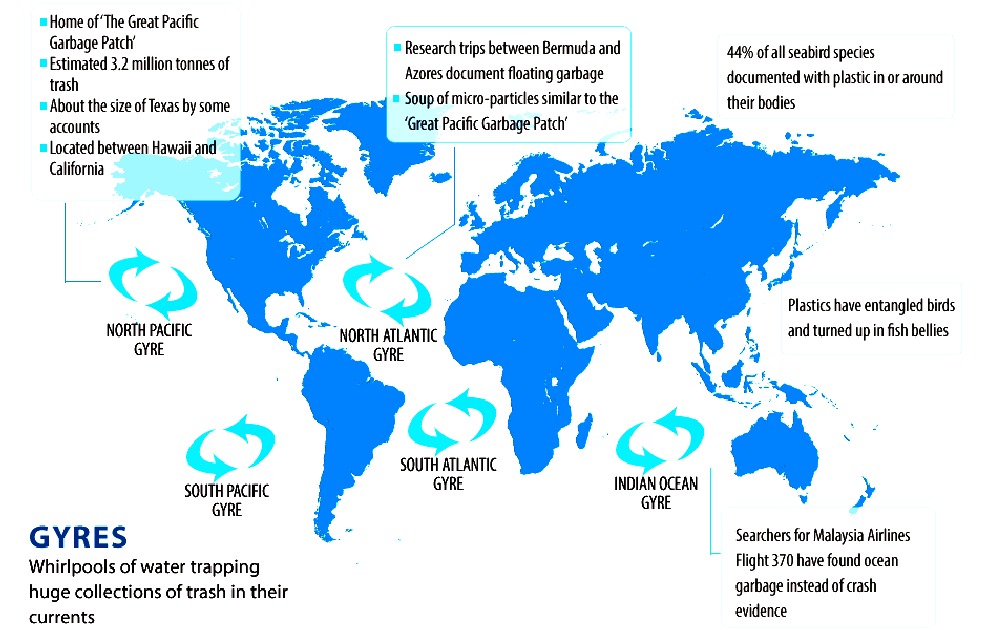
CONSERVATION
RISK
-
Plastic has accumulated in five ocean hot spots called
gyres, see here in this world map derived from information
published by 5 Gyres. The plastic is laden with toxins that
fish and marine mammals mistake for food and eat - eventually killing them.
Marine pollution is thus a major challenge if we are to ensure that species are
not wiped out.
LINKS
& REFERENCE
https://www.cbd.int/meetings/SBSTTA-01
https://worldoceanreview.com/en/wor-1/marine-ecosystem/biodiversity/
https://www.cbd.int/executive-secretary/
https://www.cbd.int/marine/

This website is
provided on a free basis as a public information service. copyright © Cleaner
Oceans Foundation Ltd (COFL) (Company
No: 4674774) 2019. Solar
Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom.
COFL is
a company without share capital.
|



